10.4: The Ideal Gas Equation - Chemistry LibreTexts

The empirical relationships among the volume, the temperature, the pressure, and the amount of a gas can be combined into the ideal gas law, PV = nRT. The proportionality constant, R, is called the …
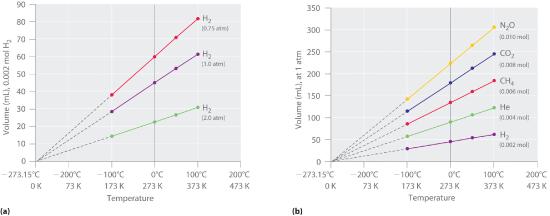
The empirical relationships among the volume, the temperature, the pressure, and the amount of a gas can be combined into the ideal gas law, PV = nRT. The proportionality constant, R, is called the gas constant. The ideal gas law describes the behavior of an ideal gas, a hypothetical substance whose behavior can be explained quantitatively by the ideal gas law and the kinetic molecular theory of gases. Standard temperature and pressure (STP) is 0°C and 1 atm.

TEST BANK chapter 5 - Test bank Chapter 5 gases 1. Which statement is false? a The density of a gas is constant as long as its temperature

Ideal Gas Law Solution
Energies, Free Full-Text

An amino acid is a compound that contains both an amine group (−NH2)
The Ideal Gas Law Boundless Chemistry
Chapter 10.3: The Ideal Gas Law - Chemistry LibreTexts

14.5 Equilibrium and Thermodynamics – Chemistry Fundamentals

The Ideal Gas Law - Chemistry LibreTexts, PDF, Gases

Gas Practice
What volume will 2.5mol of a gas occupy at 283K and at a pressure of 300torr under ideal conditions? (He also says 3 significant digits and ' (R=62.36L * torr/ (mol *
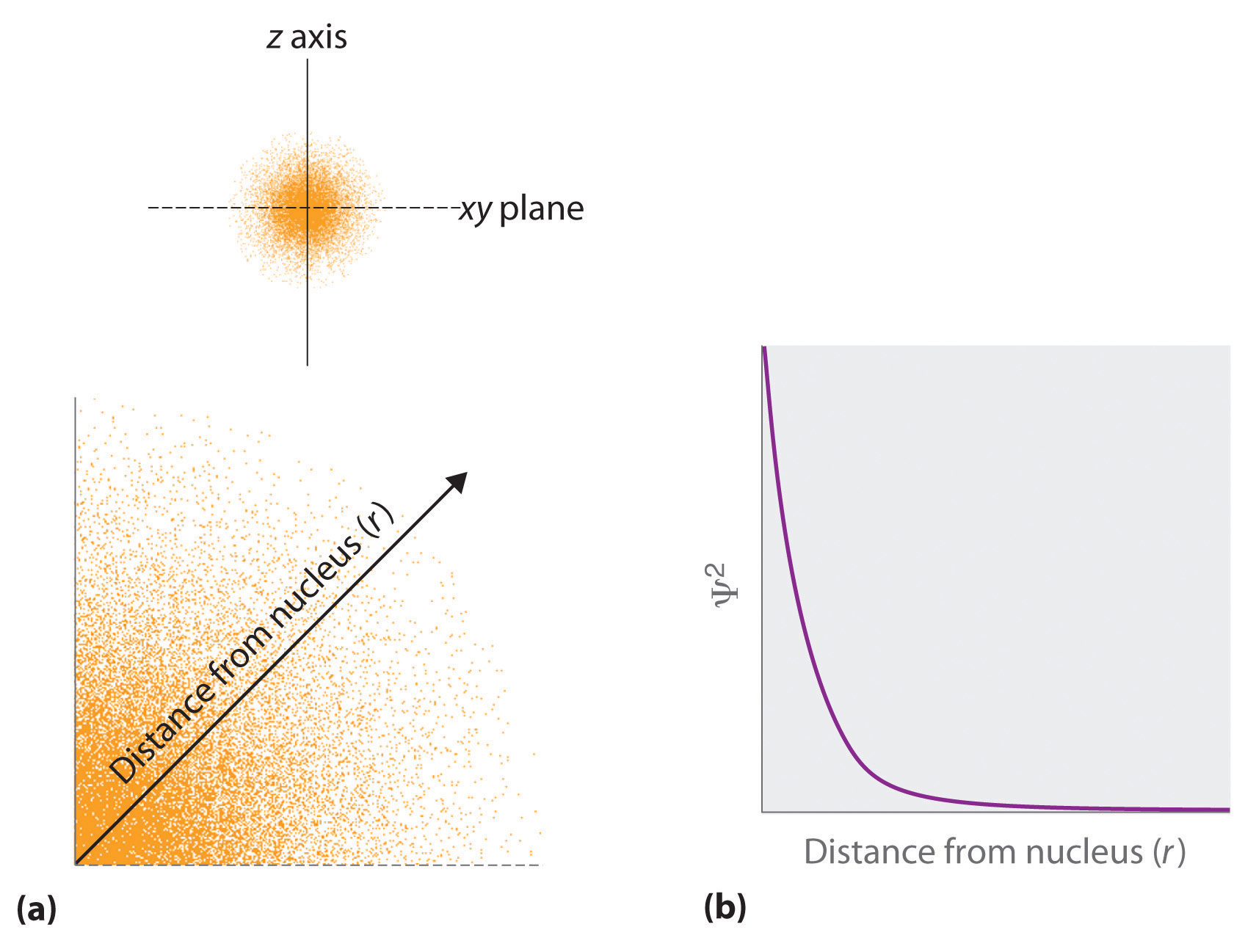
3.5 Quantum Mechanics and The Atom – Chemistry LibreTexts – Chemistry Fundamentals
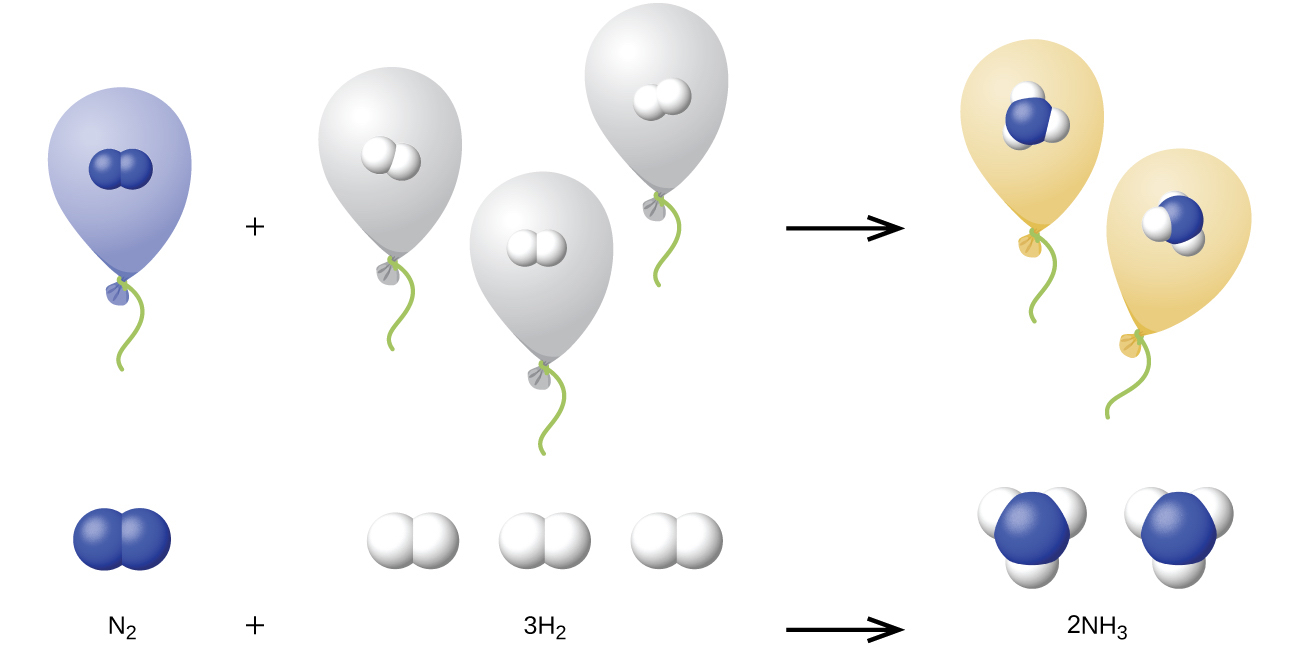
10.4: Stoichiometry of Gaseous Substances, Mixtures, and Reactions - Chemistry LibreTexts