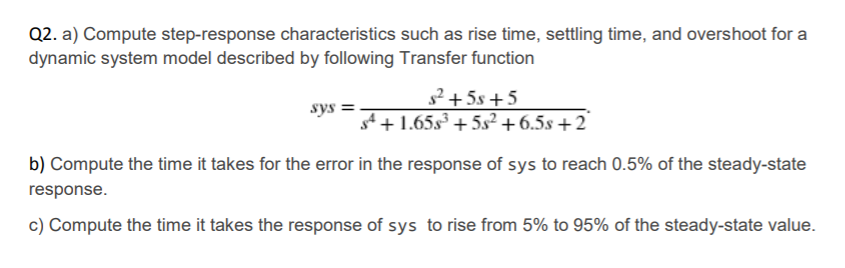
Rise time, settling time, and other step-response characteristics

stepinfo lets you compute step-response characteristics for a dynamic system model or for an array of step-response data.
Compute step-response characteristics, such as rise time, settling time, and overshoot, for a dynamic system model. For this example, use a continuous-time transfer function:
For a MIMO system, stepinfo returns a structure array in which each entry contains the response characteristics of the corresponding I/O channel of the system. For this example, use a two-output, two-input discrete-time system. Compute the step-response characteristics.
You can use SettlingTimeThreshold and RiseTimeThreshold to change the default percentage for settling and rise times, respectively, as described in the Algorithms section. For this example, use the system given by:
You can extract step-response characteristics from step-response data even if you do not have a model of your system. For instance, suppose you have measured the response of your system to a step input and saved the resulting response data in a vector y of response values at the times stored in another vector t. Load the response data and examine it.
Settling time and transient time are equal when the peak error emax is equal to the gap |yfinal-yinit| (see Algorithms), which is the case for models with no undershoot or feedthrough and with less than 100% overshoot. They tend to differ for models with feedthrough, zeros at the origin, unstable zeros (undershoot), or large overshoot.
In this example, you compute the step-response characteristics from step-response data that has an initial offset. This means that the value of the response data is nonzero before the step occurs.
Solved Q2. a) Compute step-response characteristics such as
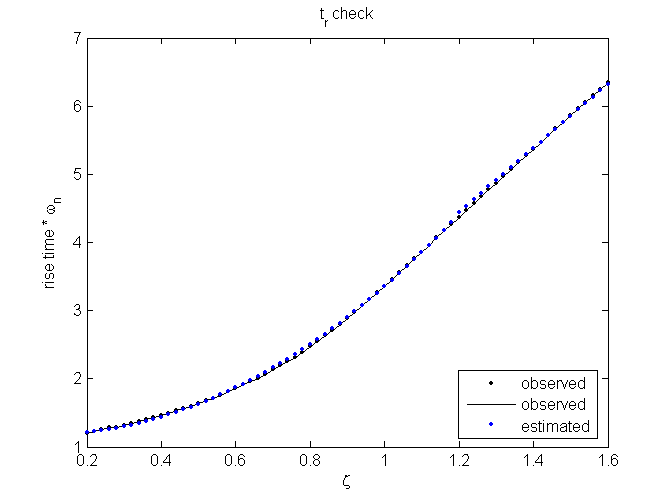
Estimating the overshoot, rise time, and settling time

Rise Time, Settling Time, and Other Step-Response Characteristics - MATLAB Stepinfo - MathWorks América Latina, PDF, Matlab

Introduction to Control Strategies

PDF) application of control system

Definition of rise time (t 1 ), settling time (t 2 ) and reaction time

Transient Response Analysis Of Control Systems - ppt download
ECE 486 Control Systems

Introduction to Control Strategies

M4A2 Lab.docx - M4A2 Lab: Control System Transient Analysis Using MATLAB Control System Transient Analysis Using MATLAB Excelsior College Prof: Jianxin

Figure 5.9 from Chapter Five 5.1 Basic Definitions
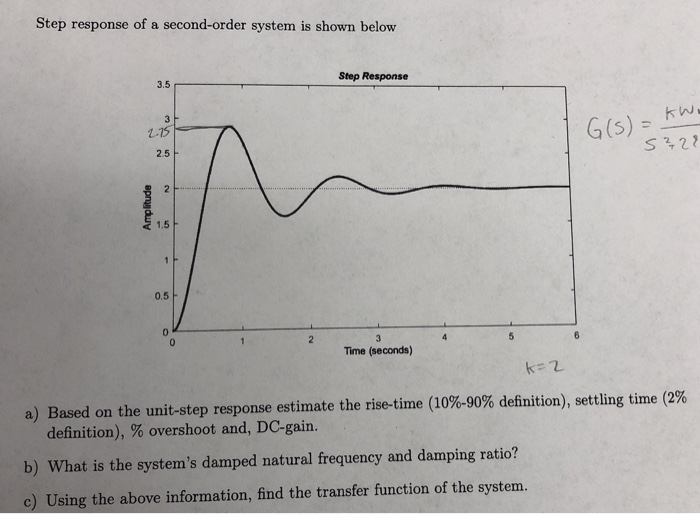
Solved Step response of a second-order system is shown below

Control Tutorials for MATLAB and Simulink - Introduction: PID Controller Design

Rise Time, Settling Time, and Other Step-Response Characteristics - MATLAB Stepinfo - MathWorks América Latina, PDF, Matlab

An intelligent tuning scheme with a master/slave approach for efficient control of the automatic voltage regulator








