Cholestasis Alters miR-34c-5p Expression in the Testes of Male Wistar Rats, Gene, Cell and Tissue
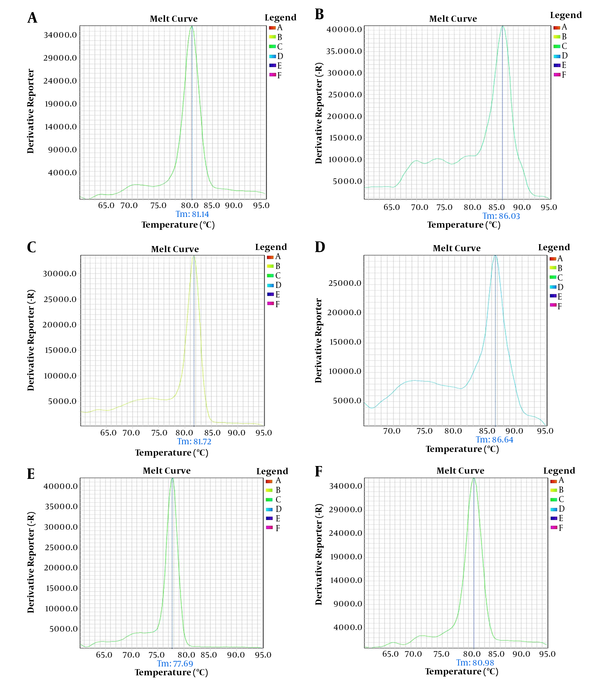
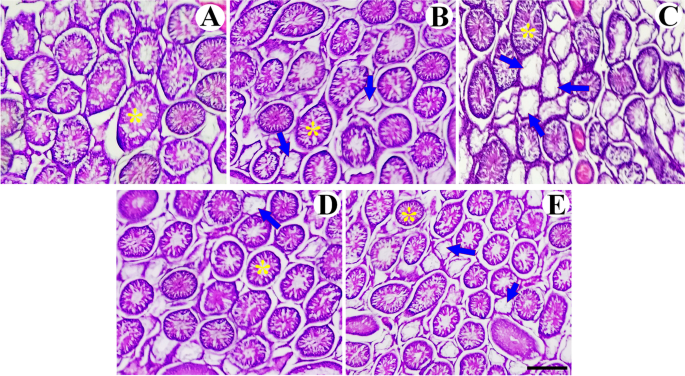
Background: Cholestasis is a pathophysiological condition, significantly reducing spermatozoa production. MiR-34c is highly expressed in adult male testicles and controls different stages of spermatogenesis. Objectives: Here, we aimed to investigate miR-34c expression in the testes of rat models of cholestasis. The expressions of THY-1, FGF-2, and CASP-3 genes, that are targeted by mirR-34c were also investigated. Methods: Cholestasis was induced in six adult rats via bile duct ligation. Four weeks after cholestasis induction, sera and testicular tissues were collected for further examinations. The levels of liver enzymes were measured using the ELISA. The structure of the testes was evaluated by histological examination. Total RNA was extracted from testes using a special kit and converted to cDNA. The expressions of miR-34c-5p, THY-1, FGF-2, and CASP-3 genes were determined by Real-Time PCR. Results: The serum levels of ALP, AST, and ALT were significantly elevated in the rat models of cholestasis (P < 0.001). Real-Time PCR revealed that the expressions of miR-34c-5p, THY-1, and FGF-2 genes decreased while CASP-3 gene was upregulated in the testes of cholestatic animals (all differences were significant at P < 0.05). Conclusions: Our study indicated that cholestasis was associated with reduced expression of miR-34c and altered expression of its target genes in the testis. Our results highlight the potential effects of cholestasis, a hepatobiliary disease, on testicular tissue function and male fertility.

NR1D2 is located in spermatogonia and declines in cryptorchidism.: (A)
Resveratrol ameliorates bisphenol A-induced testicular toxicity in adult male rats: a stereological and functional study, Basic and Clinical Andrology

THY1 is a conserved marker of undifferentiated spermatogonia in the pre-pubertal bull testis in: Reproduction Volume 139 Issue 5 (2010)

Vinclozolin-induced mouse penile malformation and “small testis” via miR132, miR195a together with the Hippo signaling pathway - ScienceDirect

Lack of Fxra Affects Meiosis Process (A) Testicular mRNA accumulation

Involvement of fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) and its receptors in the regulation of mouse sperm physiology in: Reproduction Volume 156 Issue 2 (2018)

PDF) investigating the expression of Thy1 in testis tissue of cholestatic male rats

Mouse model of cryptorchidism. a The normal (red circle) and

Homa KOUCHESFEHANI, phD, Kharazmi University, Tehran, KHU, Animal Biology

Hanieh JALALI, Professor (Assistant), Ph.D, Kharazmi University, Tehran, KHU, Department of Animal Science Biology

IJERPH October-1 2022 - Browse Articles

Homa KOUCHESFEHANI, phD, Kharazmi University, Tehran, KHU, Animal Biology

SIRT1, Interstellar Blends

Hanieh JALALI, Professor (Assistant), Ph.D, Kharazmi University, Tehran, KHU, Department of Animal Science Biology